Preventive and children's dentistry
Visiting the dentist in the early period of the child is of great importance for preserving the health of his teeth. It is best to bring the child in the period after the milk teeth have erupted, when all the teeth are healthy.
Paradontology
Gingivitis is inflammation of the gums, while periodontopathy is a disease that affects the
entire supporting apparatus of the teeth. These diseases are the most common reasons for
tooth loss in old age, and they appear more and more often in young people as well.
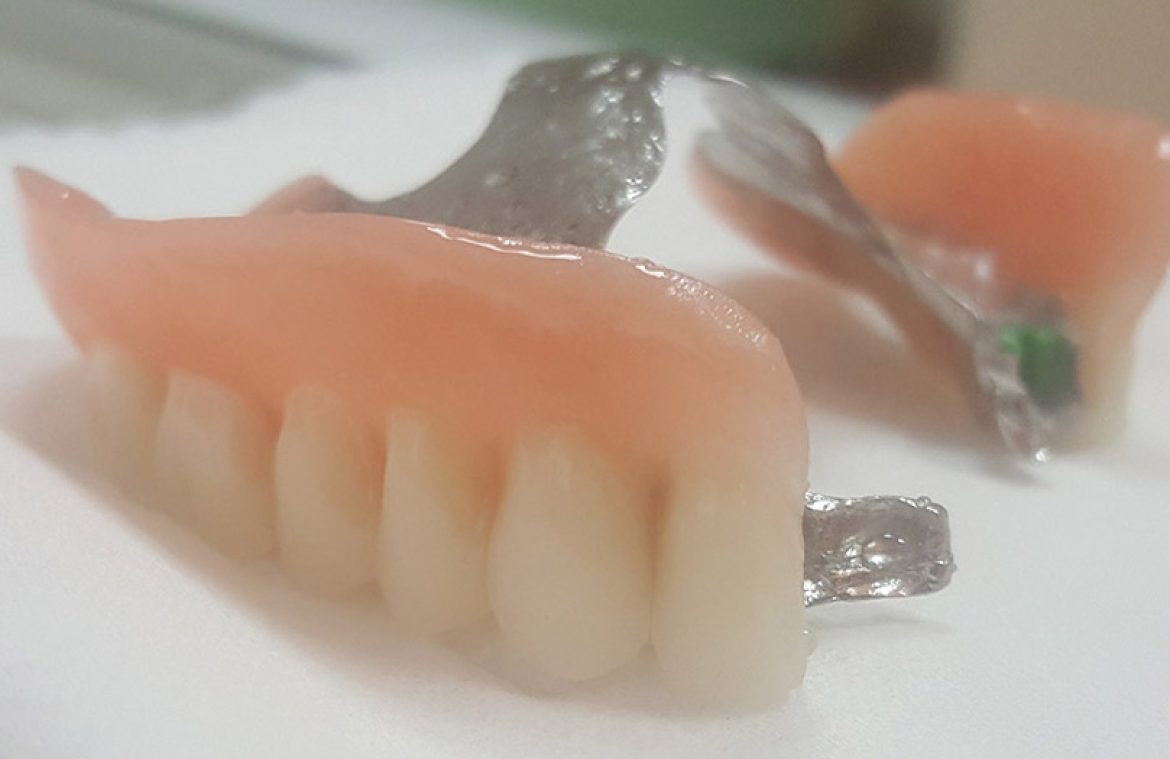
Prosthetics
Dental prosthetics provide you with compensation for damage to the tooth crown and
extracted teeth. Crowns and bridges are fixed prosthetic restorations (cemented in the
mouth and cannot be removed), while dentures are mobile.
Restorative dentistry and root canal treatment
Restorative dentistry is a branch of dentistry that deals with the treatment and replacement
of lost hard dental tissues, i.e. enamel and dentin. The loss of these structures occurs after
tooth trauma due to injuries and falls, but primarily as a consequence of the presence of
caries, which is the most common cause of dental tissue loss.
Orthodontics
Orthodontics or jaw orthopedics is a branch of dentistry that deals with improper bite that
may be the result of improper bone relationships, that is, the mutual relationship of the
upper and lower jaw, or just the improper position of the teeth in the jaws.
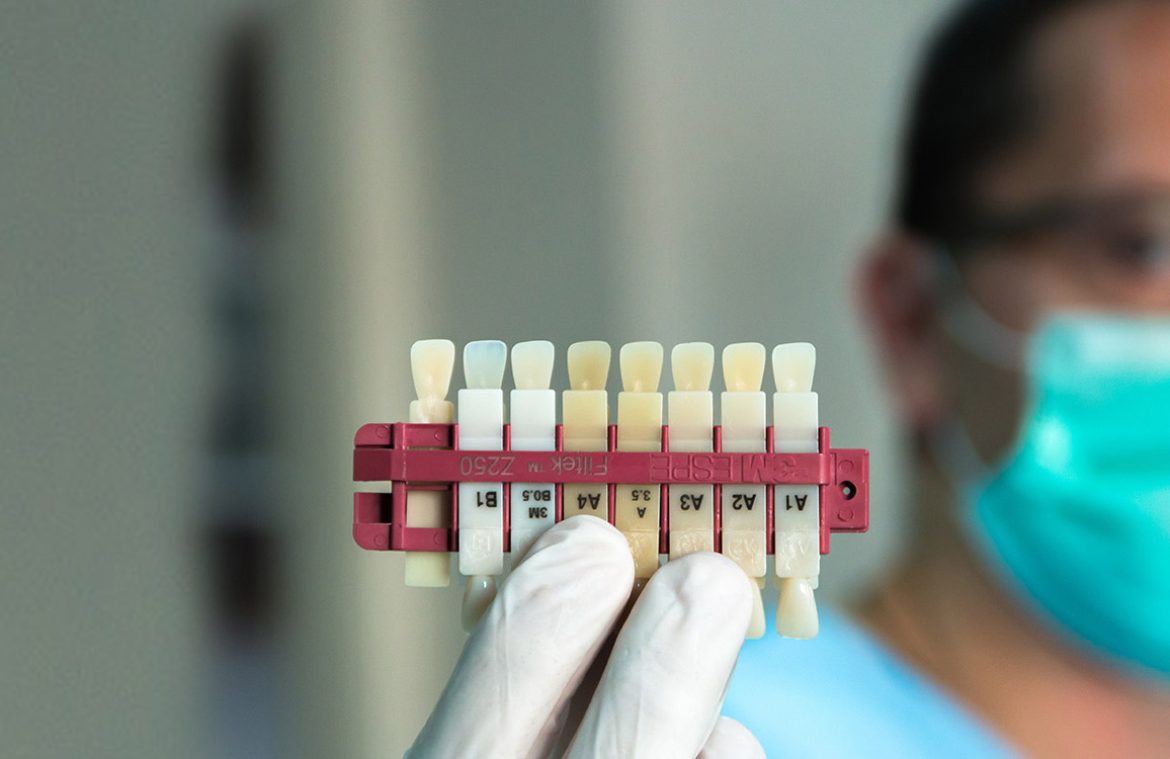
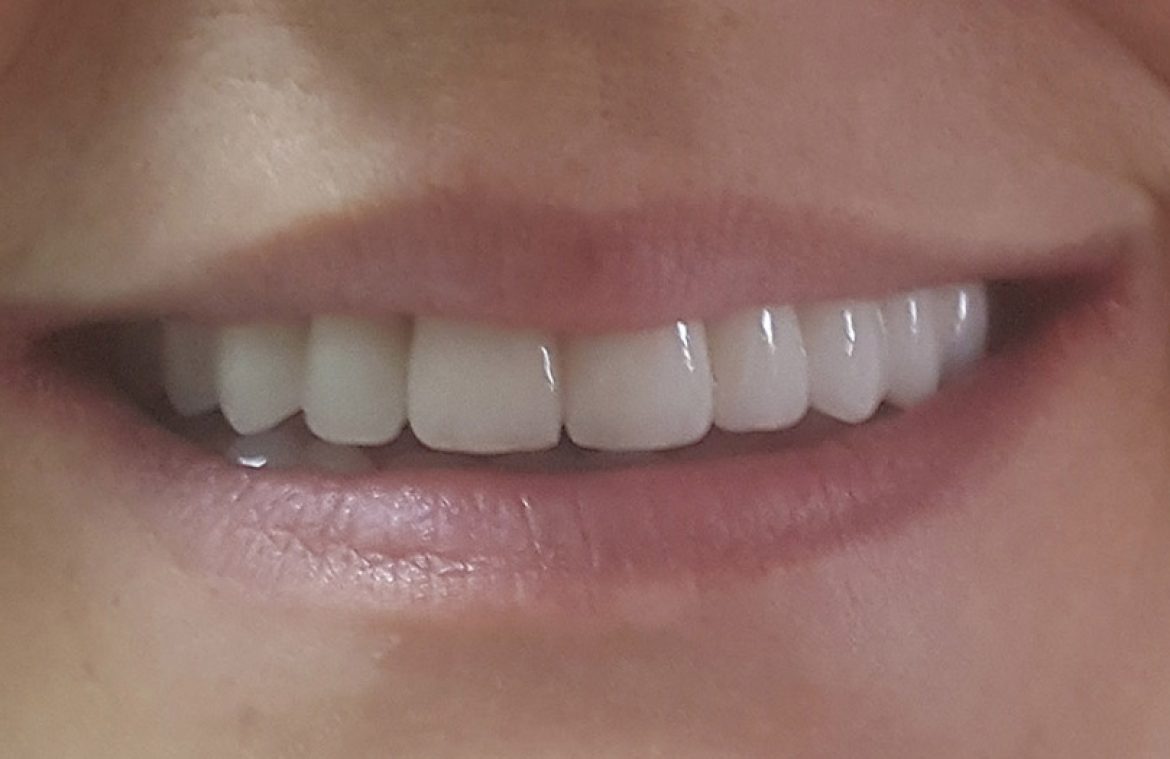
Aesthetic dentistry
Aesthetic dentistry provides solutions if your teeth have changed color or shape.
Oral surgery and implantology
Oral surgery is limited to surgery of the oral cavity, which includes surgical treatment of
inflammation in the bone of origin of the tooth (periodontitis, cysts, granulomas),
periodontal surgery, i.e. all oral-surgical procedures of the gums, whether it is about solving
inflammatory processes or functional-aesthetic defects.